# 使用 JavaScript 编写 JSON 解析器
TIP
这是翻译的一篇技术文章 (opens new window),初次翻译可能存在部分词不达意的地方,请指正。
这周 Cassidoo 周刊中的一周面试题如下所示:
编写一个函数,它接收一个合法的 JSON 字符串参数,功能是将其转换为一个对象(或者根据你所选择的语言,转换为 dicts,maps 等类型)。接收的参数如下:
fakeParseJSON('{ "data": { "fish": "cake", "array": [1,2,3], "children": [ { "something": "else" }, { "candy": "cane" }, { "sponge": "bob" } ] } } ')
最开始时,我很想这么编写:
const fakeParseJSON = JSON.parse
但是,我想到我已经写了一些关于抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree ,AST)的文章。
- 通过 Babel 创建自定义 JavaScript 语法 (opens new window)
- 编写自定义 Babel 转换的指南 (opens new window)
- 使用 JavaScript 操作 AST (opens new window)
上述文章涵盖了编译管道的综述,同样也描述了如何操作 AST,但是并没有涵盖太多关于如何实现编译的内容。
因为在一篇文章中实现 JavaScript 编译器,这对于我来说是一项艰巨的任务。
不要担心,JSON 同样也是一门语言。它有自己的语法,你可以从技术规范 (opens new window)中查阅。编写 JSON 解析器的知识和技术同样适用于编写 JS 解析器。
因此,我们开始编写 JSON 解析器吧。
# 理解语法
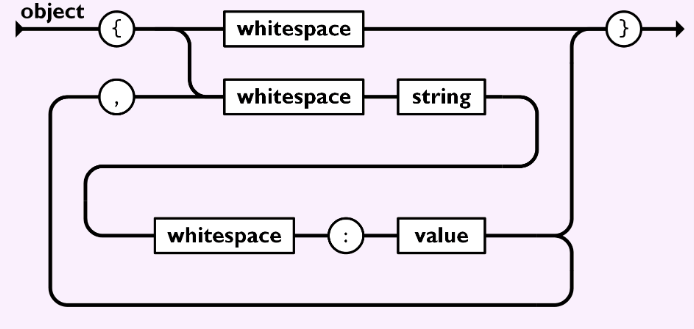
如果你查阅了技术规范 (opens new window),可以看到两个示意图:
左边的语法图(轨道图)
右边是 McKeeman 形式 (opens new window),Backus-Naur 形式(BNF)的变体
json element value object array string number "true" "false" "null" object '{' ws '}' '{' members '}'1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
上面两个表达的意思是相同的。
一个是可视化的,一个是基于文本的。基于文本的是 Backus-Naur 形式,语法中的语法,通常提供给另外一个解析器来解析此语法,并为其生成一个解析器。被称作 parser-ception !🤯
在这篇文章,我们只专注于轨道图。因为它是可视化的,利于我们理解。

图片来源:https://www.json.org/img/object.png (opens new window)
这就是 JSON 中的“object“语法。
我们从左边开始,跟着箭头,将在右边停止。
圆圈里面的是字符:{,,,:,}。方框里面的则是其他语法中的占位符:whitespace,string和value。因此要解析”whitespace",我们需要查看语法中的"whitespace"。
因此,从左边开始,对于“object”,最开始的字符必须时花括号{。然后我们在这里有两个选择:
whitespace→}→ end,或者whitespace→string→whitespace→:→value→}→ 结束
当然,当你到达”value"时,你可以选择以下两条路径:
- →
}→ end,或者 - →
,→whitespace→...→ value
然后你可以继续循环,直到你决定走第一条路径:
- →
}→ end
我认为我们现在已经熟悉了轨道图,让我们进入到下一节。
# 实现解析器
首先从下面这个结构开始:
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
let i = 0;
// TODO
}
2
3
4
我们初始化i ,作为当前字符的索引,直达i指向了str的结尾。
然后实现**“object”**语法
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
let i = 0;
function parseObject() {
if (str[i] === '{') {
i++;
skipWhiteSpace();
// if it is not '}',
// we take the path of string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ...
while (str[i] !== '}') {
const key = parseString();
skipWhiteSpace();
eatColon();
const value = parseValue();
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
在parseObject函数中,我们将会解析其他语法,如“string“ 和”whitespace“。当我们实现了它们,一切都会正常工作🤞。
我忘了一件事,忘记添加逗号,,它只有当我们开始第二次循环whitespace → string → whitespace → : → …时才会出现。
基于以上描述,我们添加以下几行代码
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
let i = 0;
function parseObject() {
if (str[i] === '{') {
i++;
skipWhiteSpace();
let initial = true;
// if it is not '}',
// we take the path of string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ...
while (str[i] !== '}') {
if (!initial) {
eatComma();
skipWhiteSpace();
}
const key = parseString();
skipWhiteSpace();
eatColon();
const value = parseValue();
initial = false;
}
// move to the next character of '}'
i++;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
一些命名约定:
- 当我们基于语法分析代码,使用返回值时,将其命名为
parseSomething - 当我们期望这里出现字符,但是不使用字符时,将其命名为
eatSomething - 当我们确定不期望这里出现字符时,将其命名为
skipSomething。
让我们来实现eatComma和eatColon函数:
function fakeParseJSON(str){
// ...
function eatComma() {
if (str[i] !== ',') {
throw new Error('Expected ",".');
}
i++;
}
function eatColon() {
if (str[i] !== ':') {
throw new Error('Expected ":".');
}
i++;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
我们已经实现了parseObject语法,但是这个解析函数的返回值是什么?
当然,我们需要返回一个 JavaScript 的对象:
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
let i = 0;
function parseObject() {
if (str[i] === '{') {
i++;
skipWhiteSpace();
const result = {};
let initial = true;
// if it is not '}',
// we take the path of string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ...
while (str[i] !== '}') {
if (!initial) {
eatComma();
skipWhiteSpace();
}
const key = parseString();
skipWhiteSpace();
eatColon();
const value = parseValue();
result[key] = value;
initial = false;
}
// move to the next character of '}'
i++;
return result;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
到目前为止,我们已经实现了”object”语法,现在是时候尝试"array"语法了:
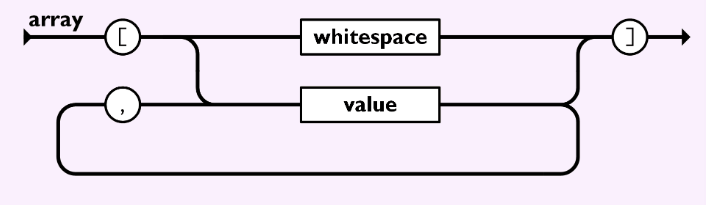
图片来源: https://www.json.org/img/array.png (opens new window)
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
// ...
function parseArray() {
if (str[i] === '[') {
i++;
skipWhitespace();
const result = [];
let initial = true;
while (str[i] !== ']') {
if (!initial) {
eatComma();
}
const value = parseValue();
result.push(value);
initial = false;
}
// move to the next character of ']'
i++;
return result;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
现在,关注于更加有趣的语法,“value":
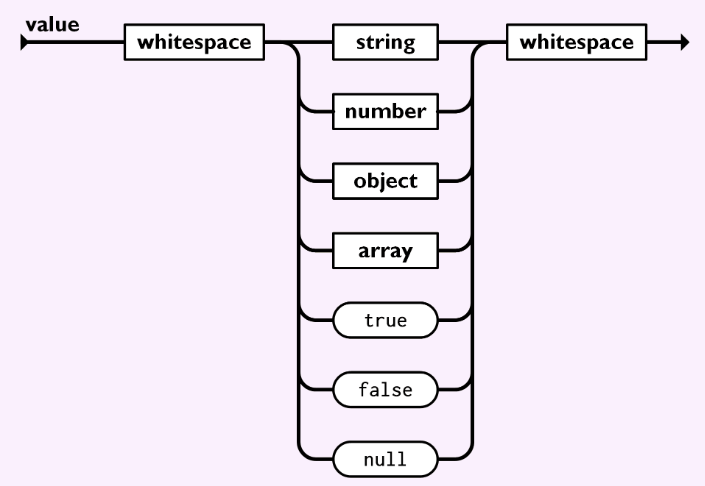
图片来源:https://www.json.org/img/value.png (opens new window)
“value”以“whitespace”为开始,然后是下面的其中一个:”string“,”number“,”object“,”array“,”true“,“false”或者”null“,然后以“whitespace”结束。
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
// ...
function parseValue() {
skipWhitespace();
const value =
parseString() ??
parseNumber() ??
parseObject() ??
parseArray() ??
parseKeyword('true', true) ??
parseKeyword('false', false) ??
parseKeyword('null', null);
skipWhitespace();
return value;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
??是 nullish coalescing operator (opens new window)(空联合操作符),它与||操作符类似。||通常被用于默认值foo || default,只有当foo是 falsey 的时候,||返回default。然而,只有当foo是null或者undefined的时候,??操作符才会返回default。
parseKeyword 函数将会检查str.slice(i)的值是否与 keyword 字符串相等,如果相等,将会返回 keyword 值。
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
// ...
function parseKeyword(name, value) {
if (str.slice(i, i + name.length) === name) {
i += name.length;
return value;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
这就是parseValue!
我们还有 3 个语法要编写,但是为了减小本篇文章的篇幅,将实现剩余的函数展示在 CodeSandBox (opens new window):
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
let i = 0;
return parseValue();
function parseObject() {
if (str[i] === "{") {
i++;
skipWhitespace();
const result = {};
let initial = true;
// if it is not '}',
// we take the path of string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ...
while (str[i] !== "}") {
if (!initial) {
eatComma();
skipWhitespace();
}
const key = parseString();
skipWhitespace();
eatColon();
const value = parseValue();
result[key] = value;
initial = false;
}
// move to the next character of '}'
i++;
return result;
}
}
function parseArray() {
if (str[i] === "[") {
i++;
skipWhitespace();
const result = [];
let initial = true;
while (str[i] !== "]") {
if (!initial) {
eatComma();
}
const value = parseValue();
result.push(value);
initial = false;
}
// move to the next character of ']'
i++;
return result;
}
}
function parseValue() {
skipWhitespace();
const value =
parseString() ??
parseNumber() ??
parseObject() ??
parseArray() ??
parseKeyword("true", true) ??
parseKeyword("false", false) ??
parseKeyword("null", null);
skipWhitespace();
return value;
}
function parseKeyword(name, value) {
if (str.slice(i, i + name.length) === name) {
i += name.length;
return value;
}
}
function skipWhitespace() {
while (
str[i] === " " ||
str[i] === "\n" ||
str[i] === "\t" ||
str[i] === "\r"
) {
i++;
}
}
function parseString() {
if (str[i] === '"') {
i++;
let result = "";
while (str[i] !== '"') {
if (str[i] === "\\") {
const char = str[i + 1];
if (
char === '"' ||
char === "\\" ||
char === "/" ||
char === "b" ||
char === "f" ||
char === "n" ||
char === "r" ||
char === "t"
) {
result += char;
i++;
} else if (char === "u") {
if (
isHexadecimal(str[i + 2]) &&
isHexadecimal(str[i + 3]) &&
isHexadecimal(str[i + 4]) &&
isHexadecimal(str[i + 5])
) {
result += String.fromCharCode(
parseInt(str.slice(i + 2, i + 6), 16)
);
i += 5;
}
}
} else {
result += str[i];
}
i++;
}
i++;
return result;
}
}
function isHexadecimal(char) {
return (
(char >= "0" && char <= "9") ||
(char.toLowerCase() >= "a" && char.toLowerCase() <= "f")
);
}
function parseNumber() {
let start = i;
if (str[i] === "-") {
i++;
}
if (str[i] === "0") {
i++;
} else if (str[i] >= "1" && str[i] <= "9") {
i++;
while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") {
i++;
}
}
if (str[i] === ".") {
i++;
while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") {
i++;
}
}
if (str[i] === "e" || str[i] === "E") {
i++;
if (str[i] === "-" || str[i] === "+") {
i++;
}
while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") {
i++;
}
}
if (i > start) {
return Number(str.slice(start, i));
}
}
function eatComma() {
if (str[i] !== ",") {
throw new Error('Expected ",".');
}
i++;
}
function eatColon() {
if (str[i] !== ":") {
throw new Error('Expected ":".');
}
i++;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
当我们完成所有的语法实现后,我们需要返回 JSON 的值,它是由parseValue返回的。
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
let i = 0;
return parseValue();
// ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
就是这样!
当然,编写这个函数并没有想象中的那么快,我们仅仅完成了基础部分,异常部分该怎么编写呢?
# 处理异常输入
作为一名优秀的开发者,我们需要优雅地处理异常部分。对于解析器,这意味着需要告诉开发者合适的错误信息。
处理 2 个常见的错误情况
- 未知字符
- 字符串意外结束
# 未知字符和字符串意外结束
在整个循环中,例如parseObject函数中的 while 循环:
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
// ...
function parseObject() {
// ...
while(str[i] !== '}') {
2
3
4
5
我们在获取字符时,需要确保没有超出字符串的长度。当字符串意外结束时会产生这种问题,然而在这个例子中,我们仍然在等待结尾字符“}”。
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
// ...
function parseObject() {
// ...
while (i < str.length && str[i] !== '}') {
// ...
}
checkUnexpectedEndOfInput();
// move to the next character of '}'
i++;
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 更进一步
你还记得作为初级开发者的时光,每当你遇到语法错误的神秘信息时,你完全没有头绪。
现在你已经有了更多的经验,是时候停止这种循环,喊叫和让用户盯着屏幕发呆了。
Unexpected token "a"
有很多方法可以优雅的处理这些错误,而不是喊叫。以下是几点建议,你可以考虑将它添加到你的编译器中。
# 错误码和标准的错误信息
返回一个标准的关键字,这对用户 Google 查询帮助很有益处。
// instead of
Unexpected token "a"
Unexpected end of input
// show
JSON_ERROR_001 Unexpected token "a"
JSON_ERROR_002 Unexpected end of input
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 更好地了解哪里出了问题
像 Babel 解析器,将会返回错误代码。这些代码通常伴随着下划线,箭头或者高亮显示,明确指出哪里出现了错误。
// instead of
Unexpected token "a" at position 5
// show
{ "b"a
^
JSON_ERROR_001 Unexpected token "a"
2
3
4
5
6
7
这是一个示例,关于如何输出代码片段:
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
// ...
function printCodeSnippet() {
const from = Math.max(0, i - 10);
const trimmed = from > 0;
const padding = (trimmed ? 3 : 0) + (i - from);
const snippet = [
(trimmed ? '...' : '') + str.slice(from, i + 1),
' '.repeat(padding) + '^',
' '.repeat(padding) + message,
].join('\n');
console.log(snippet);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 关于修复错误的建议
如果可能,最好解释哪里出现了错误并且给出修复建议。
// instead of
Unexpected token "a" at position 5
// show
{ "b"a
^
JSON_ERROR_001 Unexpected token "a".
Expecting a ":" over here, eg:
{ "b": "bar" }
^
You can learn more about valid JSON string in http://goo.gl/xxxxx
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
如果可能,建议应该基于上下文,即解析器到目前位置所收集的相关信息。
fakeParseJSON('"Lorem ipsum');
// instead of
Expecting a `"` over here, eg:
"Foo Bar"
^
// show
Expecting a `"` over here, eg:
"Lorem ipsum"
^
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
基于上下文的建议更具有相关性和可操作性。
考虑到所有的建议,通过以下几个方面检查更新后的 CodeSandbox (opens new window) :
- 有意义的错误信息
- 指出错误所在之处的代码片段
- 提供错误修复建议
function fakeParseJSON(str) {
let i = 0;
const value = parseValue();
expectEndOfInput();
return value;
function parseObject() {
if (str[i] === "{") {
i++;
skipWhitespace();
const result = {};
let initial = true;
// if it is not '}',
// we take the path of string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ...
while (i < str.length && str[i] !== "}") {
if (!initial) {
eatComma();
skipWhitespace();
}
const key = parseString();
if (key === undefined) {
expectObjectKey();
}
skipWhitespace();
eatColon();
const value = parseValue();
result[key] = value;
initial = false;
}
expectNotEndOfInput("}");
// move to the next character of '}'
i++;
return result;
}
}
function parseArray() {
if (str[i] === "[") {
i++;
skipWhitespace();
const result = [];
let initial = true;
while (i < str.length && str[i] !== "]") {
if (!initial) {
eatComma();
}
const value = parseValue();
result.push(value);
initial = false;
}
expectNotEndOfInput("]");
// move to the next character of ']'
i++;
return result;
}
}
function parseValue() {
skipWhitespace();
const value =
parseString() ??
parseNumber() ??
parseObject() ??
parseArray() ??
parseKeyword("true", true) ??
parseKeyword("false", false) ??
parseKeyword("null", null);
skipWhitespace();
return value;
}
function parseKeyword(name, value) {
if (str.slice(i, i + name.length) === name) {
i += name.length;
return value;
}
}
function skipWhitespace() {
while (
str[i] === " " ||
str[i] === "\n" ||
str[i] === "\t" ||
str[i] === "\r"
) {
i++;
}
}
function parseString() {
if (str[i] === '"') {
i++;
let result = "";
while (i < str.length && str[i] !== '"') {
if (str[i] === "\\") {
const char = str[i + 1];
if (
char === '"' ||
char === "\\" ||
char === "/" ||
char === "b" ||
char === "f" ||
char === "n" ||
char === "r" ||
char === "t"
) {
result += char;
i++;
} else if (char === "u") {
if (
isHexadecimal(str[i + 2]) &&
isHexadecimal(str[i + 3]) &&
isHexadecimal(str[i + 4]) &&
isHexadecimal(str[i + 5])
) {
result += String.fromCharCode(
parseInt(str.slice(i + 2, i + 6), 16)
);
i += 5;
} else {
i += 2;
expectEscapeUnicode(result);
}
} else {
expectEscapeCharacter(result);
}
} else {
result += str[i];
}
i++;
}
expectNotEndOfInput('"');
i++;
return result;
}
}
function isHexadecimal(char) {
return (
(char >= "0" && char <= "9") ||
(char.toLowerCase() >= "a" && char.toLowerCase() <= "f")
);
}
function parseNumber() {
let start = i;
if (str[i] === "-") {
i++;
expectDigit(str.slice(start, i));
}
if (str[i] === "0") {
i++;
} else if (str[i] >= "1" && str[i] <= "9") {
i++;
while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") {
i++;
}
}
if (str[i] === ".") {
i++;
expectDigit(str.slice(start, i));
while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") {
i++;
}
}
if (str[i] === "e" || str[i] === "E") {
i++;
if (str[i] === "-" || str[i] === "+") {
i++;
}
expectDigit(str.slice(start, i));
while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") {
i++;
}
}
if (i > start) {
return Number(str.slice(start, i));
}
}
function eatComma() {
expectCharacter(",");
i++;
}
function eatColon() {
expectCharacter(":");
i++;
}
// error handling
function expectNotEndOfInput(expected) {
if (i === str.length) {
printCodeSnippet(`Expecting a \`${expected}\` here`);
throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0001 Unexpected End of Input");
}
}
function expectEndOfInput() {
if (i < str.length) {
printCodeSnippet("Expecting to end here");
throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0002 Expected End of Input");
}
}
function expectObjectKey() {
printCodeSnippet(`Expecting object key here
For example:
{ "foo": "bar" }
^^^^^`);
throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0003 Expecting JSON Key");
}
function expectCharacter(expected) {
if (str[i] !== expected) {
printCodeSnippet(`Expecting a \`${expected}\` here`);
throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0004 Unexpected token");
}
}
function expectDigit(numSoFar) {
if (!(str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9")) {
printCodeSnippet(`JSON_ERROR_0005 Expecting a digit here
For example:
${numSoFar}5
${" ".repeat(numSoFar.length)}^`);
throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0006 Expecting a digit");
}
}
function expectEscapeCharacter(strSoFar) {
printCodeSnippet(`JSON_ERROR_0007 Expecting escape character
For example:
"${strSoFar}\\n"
${" ".repeat(strSoFar.length + 1)}^^
List of escape characters are: \\", \\\\, \\/, \\b, \\f, \\n, \\r, \\t, \\u`);
throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0008 Expecting an escape character");
}
function expectEscapeUnicode(strSoFar) {
printCodeSnippet(`Expect escape unicode
For example:
"${strSoFar}\\u0123
${" ".repeat(strSoFar.length + 1)}^^^^^^`);
throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0009 Expecting an escape unicode");
}
function printCodeSnippet(message) {
const from = Math.max(0, i - 10);
const trimmed = from > 0;
const padding = (trimmed ? 4 : 0) + (i - from);
const snippet = [
(trimmed ? "... " : "") + str.slice(from, i + 1),
" ".repeat(padding) + "^",
" ".repeat(padding) + message
].join("\n");
console.log(snippet);
}
}
// console.log("Try uncommenting the fail cases and see their error message");
// console.log("↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓");
// Fail cases:
printFailCase("-");
printFailCase("-1.");
printFailCase("1e");
printFailCase("-1e-2.2");
printFailCase("{");
printFailCase("{}{");
printFailCase('{"a"');
printFailCase('{"a": "b",');
printFailCase('{"a":"b""c"');
printFailCase('{"a":"foo\\}');
printFailCase('{"a":"foo\\u"}');
printFailCase("[");
printFailCase("[][");
printFailCase("[[]");
printFailCase('["]');
function printFailCase(json) {
try {
console.log(`fakeParseJSON('${json}')`);
fakeParseJSON(json);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
# 总结
为了实现解析器,你必须从语法部分开始。
你可以通过轨道图或者 Backus-Naur Form 使语法正式化,设计语法是最难的一部分操作。
一旦你解决了语法,你就可以基于语法实现解析器。
异常处理是非常重要的,其中最重要的是有意义的错误信息,从而用户知道如何修复。
现在你已经知道如何实现一个简答的解析器了,是时候着眼于复杂的解析器了
最后,请关注 @cassidoo (opens new window),她的周刊令人惊叹!
