# 基本数据结构与算法
众所周知,Node.js 遵循的是 CommonJS 规范进行模块化开发,因为 ES6 在 JavaScript 标准中引入了官方的模块功能。因此,在这里都是用的是 ES6 模块导出。点击查看相关差别及使用方法 (opens new window)。
由于 Node 中,ES6 导入还是一个实验功能,因此我们需要将文件扩展名由 js 修改为 mjs,并在 node 命令后添加 --experimental-modules 来执行代码。
# 栈
栈是一种遵循 后进先出(LIFO) 原则的有序集合。新添加或待删除的元素都保存在栈的一端,被称作栈顶,另一端叫做栈底。
栈中的方法一般有:
push(elements):添加一个或多个新元素到栈顶pop():移除栈顶的元素,同时返回被移除的元素peek():返回栈顶的元素,不对栈做任何修改(仅仅是返回)isEmpty():判断栈里是否存在元素,没有则返回 true,否则返回 falseclear():移除栈里所有的元素size():返回栈里的元素个数。该方法与数组中的 length 属性类似
我们可以通过数组来实现栈,但是其大部分的方法的时间复杂度为 O(n),且为了保证其元素排列有序,他会占用更多的内存空间。因此我们可以选择使用对象来实现栈。
# 对象实现 Stack 类
首先我们要声明一个 Stack 类,并实现栈应有的方法即可,最终代码如下
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.count = 0;
this.items = {};
}
isEmpty() {
return this.count === 0;
}
size() {
return this.count;
}
clear() {
this.count = 0;
this.items = {};
}
push(item) {
this.items[this.count] = item;
this.count++;
}
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
this.count--;
const result = this.items[this.count];
delete this.items[this.count];
return result;
}
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
return this.items[this.count - 1];
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
let objString = `${this.items[0]}`;
for (let i = 1; i < this.count; i++) {
objString += `,${this.items[i]}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
这里我们创建了 toString 方法,从而可以打印出栈的内容,除了该方法之外,其余的方法复杂度均为 O(1)
# 保护数据结构的内部元素
在创建别的开发这也可以使用的数据结构或者对象时,我们希望保护内部的元素,只有暴露出来的方法才能修改内部结构。但是 ES6 中的类时基于原型的,这就代表无法声明私有变量或者方法。因此只能使用以下方法来实现:
- 下划线命名约定,来标价一个属性为私有属性(实际上并不能保护数据)。
- 使用 Symbol 实现类,但这实际上仍然会被破坏,详见 stackSymbol (opens new window) 文件。
- 使用 ES6 的 WeakMap 实现类,WeakMap 可以存储键值对,其中键是对象,值可以是任意数据,但采用这种方法,代码的可读性不强,且扩展该类时无法继承私有属性。详见 stackWeakMap (opens new window) 文件。
# 相关问题
我们可以通过栈来存储访问过的任务、路径或撤销的操作。这里我们只是简单介绍其解决十进制转二进制的问题,以及任意进制转换的算法。
function decimalToBinary(decNumber) {
const remStack = new Stack();
let number = decNumber;
let rem;
let binaryString = "";
while (number > 0) {
rem = Math.floor(number % 2);
remStack.push(rem);
number = Math.floor(number / 2);
}
while (!remStack.isEmpty()) {
binaryString += remStack.pop().toString();
}
return binaryString;
}
console.log(decimalToBinary(233)); // 11101001
console.log(decimalToBinary(10)); // 1010
console.log(decimalToBinary(1000)); // 1111101000
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 队列和双端队列
# 队列
队列遵循 先进先出(FIFO) 原则的一组有序的项。队列在尾部添加新元素,并从顶部移除元素。现实中,最常见的队列就是排队。
队列中一般可用的方法有:
enqueue(element(s)):向队列尾部添加一个( 或多个 )新的元素。dequeue():移除队列的第一项( 排在最前面的一项 )并返回被移除的元素。peek():返回队列中的第一个元素。isEmpty():队列中不包含任何元素,返回 true,否则返回 false。size():返回队列中包含的元素个数。clear():清除队列中的元素。toString():返回队列的内容。
与栈类似,我们也可以通过数组来实现队列,但是为了获取元素更高效,我们同样通过对象来实现队列。
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
this.count = 0;
this.lowestCount = 0; // 用来追踪第一个元素
}
size() {
return this.count - this.lowestCount;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
// 添加新的项
enqueue(item) {
this.items[this.count] = item;
this.count++;
}
// 移除队列第一项
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
const result = this.items[this.lowestCount];
delete this.items[this.lowestCount];
this.lowestCount++;
return result;
}
// 返回第一项
peek() {
return this.items[this.lowestCount];
}
// 清空队列
clear() {
this.items = {};
this.count = 0;
this.lowestCount = 0;
}
// 添加 toString 方法
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
let objString = `${this.items[this.lowestCount]}`;
for (let i = this.lowestCount + 1; i < this.count; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${this.items[i]}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
# 双端队列
双端队列( deque,或称 double-ended queue )是把队列和栈相结合的一种数据结构。同时遵循了先进先出和后进先出的原则。例如电影中的队伍,一个刚买票的人如果只是需要简单询问信息,可以直接回到队伍头部。另外,在队伍末尾的人如果赶时间,他可以直接离开队伍。
双端队列中的方法有:
addFront(element):该方法在双端队列前端添加新的元素。addBack(element):该方法在双端队列后端添加新的元素(实现方法和 Queue 类中的 enqueue 方法相同)。removeFront():该方法会从双端队列前端移除第一个元素(实现方法和 Queue 类中的 dequeue 方法相同)。removeBack():该方法会从双端队列后端移除第一个元素(实现方法和 Stack 类中的 pop 方法一样)。peekFront():该方法返回双端队列前端的第一个元素(实现方法和 Queue 类中的 peek 方法一样)。peekBack():该方法返回双端队列后端的第一个元素(实现方法和 Stack 类中的 peek 方法一样)。isEmpty()、size()、clear()和toString()方法
class Deque {
constructor() {
this.items = {};
this.count = 0;
this.lowestCount = 0;
}
size() {
return this.count - this.lowestCount;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
clear() {
this.items = {};
this.count = 0;
this.lowestCount = 0;
}
addBack(item) {
this.items[this.count] = item;
this.count++;
}
addFront(item) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.addBack(item);
} else if (this.lowestCount > 0) {
this.lowestCount--;
this.items[this.lowestCount] = item;
} else {
for (let i = this.count; i > 0; i--) {
this.items[i] = this.items[i - 1];
}
this.count++;
this.lowestCount = 0;
this.items[0] = item;
}
}
removeBack() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
this.count--;
const result = this.items[this.count];
delete this.items[this.count];
return result;
}
removeFront() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
const result = this.items[this.lowestCount];
delete this.items[this.lowestCount];
this.lowestCount++;
return result;
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
let objString = `${this.items[this.lowestCount]}`;
for (let i = this.lowestCount + 1; i < this.count; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${this.items[i]}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
# 相关问题
# 击鼓传花
在队列实际应用过程中,我们会使用一些修改版本,其中就有循环队列,其中的典型的例子就是击鼓传花游戏。一群人围成一圈,把花尽快的传递到旁边的人,停止的时候花在谁手上就淘汰谁,直至剩下最后一人。
循环队列-击鼓传花游戏 (opens new window)
# 回文检查器
回文是正反都能读通的单词、词组、数或一系列字符的序列,例如 madam 或 racecar。
# 链表
由于数组的大小是固定的,从数组的起点或中间插入或移除项的成本很高,需要移动元素。( JavaScript 内部实现同样如此。)
链表存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用( 也称指针或链接 )组成。
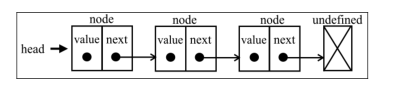
链表的好处在于,添加或移除元素的时候不需要移动其他元素,然而链表需要使用指针,因此想要访问链表中间的一个元素,则需要从起点( 表头 )开始迭代链表直到找到所需的元素。就像寻宝元素一样,你只能从第一条线索顺着往下找。
# 单向链表
下面是 LinkedList 类的 ”骨架“。
import { defaultEquals } from "../util.mjs";
import { Node } from "../models/LinkedListModels.mjs";
class LinekedList {
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
this.count = 0; // 链表中存储的数量
this.head = undefined; // 第一个元素的引用
this.equalsFn = equalsFn; // 用于比较链表中的元素是否相同,也可以实例化时自行传
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这里默认的比较函数写在 util 文件中,便于复用:
export function equalsFn(a, b) {
return a === b;
}
2
3
然后需要一个助手类,用于表示链表中的元素:
export class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element; // 要加入链表中元素的值
this.next = undefined; // 链表中下一个元素的指针
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
链表所需要的方法:
push(element) :向链表尾部添加一个新元素。
insert(element, position) :向链表的特定位置插入一个新元素。
getElementAt(index):返回链表中特定位置的元素。如果链表中不存在这样的元素,
则返回 undefined 。
remove(element) :从链表中移除一个元素。
indexOf(element) :返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素则返回 -1 。
removeAt(position) :从链表的特定位置移除一个元素。
isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回 true ,如果链表长度大于0则返回 false 。
size() :返回链表包含的元素个数,与数组的 length 属性类似。
toString() :返回表示整个链表的字符串。由于列表项使用了 Node 类,就需要重写继
承自 JavaScript 对象默认的 toString 方法,让其只输出元素的值。
点击查看链表数据结构代码实现 (opens new window)
# 双向链表
双向链表与单向链表的区别在于,单向链表中,一个节点只有对下一个节点的引用;而在双向链表中,引用是双向的,一个链向下一个节点,一个链向上一个节点。因此,在双向链表中进行删除或者添加节点时,其要比单向链表复杂的多。如下图所示:

首先我们先根据单向链表实现 DoublyLinkedList 类
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
super(equalsFn);
this.tail = undefined; // 链表最后一个元素的引用
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
同样,我们需要一个双向节点的助手类,其继承自 Node 类,并对 Node 类改造如下:
export class Node {
constructor(element, next) {
this.element = element; // 要加入链表中元素的值
this.next = next; // 链表中下一个元素的指针
}
}
export class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(element, next, prev) {
super(element, next);
this.prev = prev; // 链表中上一元素的指针
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
这里我们主要介绍其重写的插入和移除元素的方法,双向链表与单向链表相比,多了控制前一个(prev)指针,其主要实现如下:
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new DoublyNode(element);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
// 如果不存在首节点
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
node.next = this.head;
current.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
} else if (index === this.count) {
// 在最后进行插入
current = this.tail;
node.prev = current;
current.next = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
curernt = previous.next;
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt (index) {
if (this.count === 0) {
return undefined
}
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
// 如果只有一个元素
if (this.count === 1) {
this.tail = undefined
} else {
this.head.prev = undefined
}
} else if (index === this.count - 1) {
// 移除最后一个元素
current = this.tail
this.tail = current.prev
this.tail.next = undefined
} else {
current = this.getElementAt(index)
const previous = current.prev
// 将previous 的下一项与 current 的下一项链接起来,跳过current
previous.next = current.next
current.next.previous = previous
}
this.count--;
return current.element
}
return undefined
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
其内部还增加了 getTail 和 inverseToString 方法,具体可以查看代码 (opens new window)。
# 循环链表
循环列表可以向链表一样只有单向引用,也可以像双向链表一样有双向引用。循环链表和链表中的唯一区别在于,最后一个元素指向下一个元素的指针(tail.next)不是引用 undefined ,而是指向第一个元素。
双向循环列表则是有指向 head 元素的 tail.next 和指向 tail 元素的 head.prev。
这里我们主要编写的是单向循环列表,首先创建 CircularLinkedList 类:
export class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
super(equalsFn)
}
}
2
3
4
5
同样我们主要介绍其插入元素和删除元素的实现方法,主要是对最后一个元素进行处理。
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(element);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
// 没有元素
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
node.next = this.head;
} else {
node.next = current;
// 获取最后一个元素, 正常获取最后一个元素应该是 this.size() - 1
// 这里使用 this.sizez() 是因为已经多了新增的 node 元素
current = this.getElementAt(this.size());
this.head = node;
// 将最后一个元素指向第一个元素
current.next = this.head;
}
} else {
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.mext = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.size() === 1) {
this.head = undefined;
} else {
const removed = this.head;
// 最后一个元素
current = this.getElementAt(this.size() - 1);
this.head = removed.next;
current.next = this.head;
current = removed
}
} else {
// 不需要改变循环列表的最后一个元素
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1)
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next
}
this.count--;
return current.element
}
return undefined
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
其内部还重写了 push 方法,具体可以查看代码 (opens new window)。
# 有序链表
有序链表是指保持元素有序的链表结构,我们插入元素时,也需要将元素插入到正确的位置,来保证链表的有序性。
首先我们需要定义一个自定义的比较函数 defaultCompare
export const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1
}
export function defaultCompare (a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return 0
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
然后声明 SortedLinkedList 类,骨架如下所示:
export class SortedLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals, compareFn = defaultCompare) {
super(equalsFn);
this.compateFn = compareFn;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
接下来我们来编写 insert 方法来覆盖其默认方法
insert(element) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
super.insert(element, 0);
} else {
const pos = this.getIndexNextSortedElement(element);
super.insert(element, pos);
}
}
getIndexNextSortedElement(element) {
let current = this.head;
let i = 0;
for (; i < this.size() && current; i++) {
const compare = this.compateFn(element, current.element);
if (compare === Compare.LESS_THEN) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
return i;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
由于我们需要保持元素具有一定的顺序,因此我们指将元素插入到指定位置,同理 push 方法与 insert 方法其实是相同的。
# 集合
集合是一组无序且唯一的项组成。这里我们将从头模拟创建 Set 类,并实现原生 Set 类所没有提供的集合运算,如并集、交集和差集。
export class _Set {
constructor() {
this.set = Object.create(null);
}
add(key) {
this.set[key] = true;
}
has(key) {
return this.set[key] === true;
}
delete(key) {
if (this.has(key)) {
delete this.set[key];
return true;
}
return false;
}
clear() {
this.set = Object.create(null);
}
// 自定义size 方法
size() {
return Object.keys(this.set).length;
}
values() {
return Object.keys(this.set);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 并集
对于给定的两个集合,返回包含两个集合中所有元素的新集合
union(otherSet) {
const unionSet = new _Set();
this.values().forEach((key) => unionSet.add(key));
otherSet.values().forEach((key) => unionSet.add(key));
return unionSet;
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 交集
对给定两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中共有元素的新集合。
intersection(otherSet) {
const intersectionSet = new _Set();
// 减少循环次数
const values = this.values();
const otherValues = otherSet.values();
let smallValues = values;
let biggerSet = otherSet;
if (values.length > otherValues.length) {
smallValues = otherValues;
biggerSet = this;
}
smallValues.forEach((key) => {
if (biggerSet.has(key)) {
intersectionSet.add(key);
}
});
return intersectionSet;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 差集
对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含所有存在于第一个集合而不存在于第二个集合的元素的新集合。
difference (otherSet) {
const diffSet = new _Set()
this.values().forEach(key => {
if (!otherSet.has(key)) {
diffSet.add(key)
}
})
return diffSet;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 子集
验证一个给定集合是否是另一个集合的子集。
isSubsetOf(otherSet) {
if (this.size() > otherSet.size()) {
return false;
}
const values = this.values()
for (let i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
if (!otherSet.has(values[i])) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
以上就是我们模拟的 Set 集合,具体详见代码 (opens new window)。 ES2015 已经有原生的 Set 类供我们使用,具体查看文档 (opens new window)。
# 字典和散列表
# 字典
从上文可知集合是用来表示一组不重复的元素。在字典中,存储的[键,值]对,其中键名用来查询特定元素。字典也称作为映射或关联数组。
ES6 中的 Map 类即我们所说的字典。
首先我们来实现 Dictionary 类的骨架:
import { defaultToString } from '../util.mjs'
export class Dictinoary {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
这里 defaultToString 是我们定义的工具函数,作用是将 key 转换为字符串,如果直接通过 [键] 来设置是不友好的,因为对于对象作为键的时候,会变成 [object Object]。
export function defaultToString (item) {
if (item === null) {
return 'UNLL'
} else if (item === undefined) {
return 'UNDEFINED'
} else if (typeof item === 'string' || item instanceof String) {
return `${item}`
}
return item.toString();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
字典所能使用的方法如下所示:
set(key,value):向字典中添加新元素。如果key已经存在,则进行覆盖。delete(key):通过使用键值来从字典中移除键值对应的数据值。has(key):如果某个键值存在于这个字典中,则返回 true,反之则返回 false。get(key):通过键值查找特定的数值并返回。clear():将这个字典中的所有元素全部删除。size():返回字典所包含元素的数量。与数组的 length 属性类似。isEmpty():在 size 为零的时候返回 true,否则返回 false。keys():将字典所包含的所有键名以数组形式返回。values():将字典所包含的所有数值以数组形式返回。keyValues():将字典中所有的[键,值]对返回。forEach(cb):迭代字典中所有的简直对。cb 函数有两个参数:key 和 value。该方法可以在回调函数返回 false 时被中止(类似 Array 中的 every 方法)。
在字典中我们通过 ValuePair 类来设置键和值。为了保存信息的需要我们会同时保存 key 和 value,同时提供 toString 方法。
export class ValuePair {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
toString() {
return `[#${this.key}: ${this.value}]`;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
最后我们编写的 Dictionary 类如下所示:
import { defaultToString } from "../util.mjs";
import { ValuePair } from "../models/ValuePair.mjs";
export class Dictinoary {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {};
}
has(key) {
return this.table[this.toStrFn[key]] != null;
}
set(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const tableKey = this.toStrFn[key];
this.table[tableKey] = new ValuePair(key, value);
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key) {
const valuePair = this.table[this.toStrFn[key]];
return valuePair == null ? undefined : valuePair.value;
}
delete(key) {
if (this.has(key)) {
delete this.table[this.toStrFn[key]];
return true;
}
return false;
}
keyValues() {
return Object.values(this.table);
}
values() {
return this.keyValues().map((valuePair) => valuePair.value);
}
keys() {
return this.keyValues().map((valuePair) => valuePair.key);
}
forEach (cb) {
const valuePairs = this.keyValues();
for (let i = 0, len = valuePairs.length; i < len; i++){
const result = cb(valuePairs[i].key, valuePairs[i].value);
if (result === false) {
break;
}
}
}
size() {
return this.keyValues().length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
const valuePairs = this.keyValues();
let objString = `${valuePairs[0].toString()}`;
for (let i = 1, len = valuePairs.length; i < len; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${valuePairs[i].toString()}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
验证相关详见代码文件 (opens new window)。
1089.复写零 →
